Bitcoin has captured attention across the globe, sparking interest from financial analysts, tech lovers, and everyday folks alike. Whether you are deep into investing or just starting to explore the crypto space, getting a grasp on Bitcoin is more relevant than ever.
Here’s a breakdown of the key things to know from where it all began, to how mining works, how transactions happen, and everything in between.
The Rise of Bitcoin and Its Creator: Satoshi Nakamoto
In October 2008, an individual (or group) under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published a groundbreaking white paper titled Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.
This paper outlined the concept of a decentralized digital currency, free from government or financial institution control.
But who exactly is Satoshi Nakamoto?
Despite various claims and speculations, Nakamoto’s identity remains a mystery.
Some believe it’s a pseudonym to protect their privacy, while others suggest it could be a collective effort.

What Is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is the first and most popular cryptocurrency, a form of digital currency that operates on blockchain technology.
Cryptocurrency is a digital currency in which transactions are verified and records maintained by a decentralized system using cryptography, rather than by a centralized authority.
Unlike traditional money, Bit-coin exists solely in the digital world, with transactions secured by cryptography.
- Decentralization: Banks or governments do not control it’s transactions. It is a form of cryptocurrency which relies on blockchain technology. By means of cryptocurrency or crypto (short form of cryptocurrency), it is a digital currency or digital money that uses cryptography to secure its currency transactions.
- Blockchain: A public ledger records all Bitcoin transactions, ensuring transparency. As it is a digital currency there is no physical transaction and you will not find any physical coin of it. Users conduct all transactions in the virtual world, record them in a ledger called the Blockchain, and share it among themselves. It is just data.
- Limited Supply: There will only ever be 21 million Bitcoins, adding to its scarcity and value. Thus it is a full-proof system in terms of digital transactions.
How Does Bitcoin Work?
Bit-coin transactions occur in the digital realm. Here’s how it works:
- Digital Wallets: To use Bitcoin, both the sender and receiver must have digital wallets.
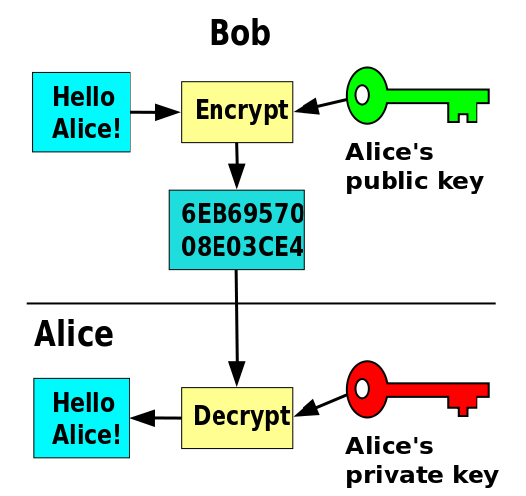
- Public and Private Keys: You authenticate transactions using a private key (your unique signature) and send them to a public key (the recipient’s address).
- Blockchain Recording: Once the system verifies the transaction, it adds it to the blockchain, ensuring no one can alter it.
For instance, if you want to buy a laptop using Bitcoin, the seller provides their public key. You initiate the payment using your private key, and the system records the transaction on the blockchain.
Bitcoin Transactions Explained
- Basically, to use it, you need to own some, you can buy it from others using physical currency, or mine it yourself by solving a mathematical puzzle.
- Now to earn Bitcoin some people do mining! What happens that every ten minutes or so mining computers collect a few hundred pending bitcoin transactions (a “block”) and turn them into a mathematical puzzle? The miner who solves the puzzle earns 25 coins as a reward. Miners generate new Bitcoins, but only after the ledger adds 99 more blocks.
- Thus by solving mathematical puzzles you can earn Bitcoin but it is not easy. As sometimes the expense on computers (it can be a computer network) and electric power is much higher than the market value of earned Bitcoin. Still, some people actively mine it as part of the Bitcoin network.
- There are so many websites and companies that help your mining activity by charging you some fees just like banks.
Bitcoin Mining: How New Bitcoins Are Created
It is a process where powerful computers (or networks) solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. Miners receive Bitcoin as a reward for their efforts.
Key Points About Mining:
- Reward System: Miners receive Bit-coin as a reward for solving puzzles. Initially, the system rewarded miners with 50 BTC, but it halves this amount approximately every four years (currently the system rewards 6.25 BTC per block).
- High Costs: Mining requires expensive hardware and consumes significant electricity, which can sometimes outweigh the value of the Bitcoin earned.
- Bitcoin Supply Cap: Only 21 million Bitcoins will ever exist. As of now, miners have mined over 19 million Coins.

Why Is Bitcoin So Valuable?
Scarcity, utility, and demand drive It’s value. With only 21 million Bitcoins in existence, its limited supply contributes to its high price. In January 2025, it reached an all-time high of nearly $106,963 USD per Bitcoin.
Factors Influencing Bitcoin’s Value:
- Scarcity: Finite supply of 21 million Bitcoins.
- Adoption: Increasing acceptance by individuals, companies, and even governments.
- Security: Blockchain ensures secure and tamper-proof transactions.
- Inflation Hedge: Bitcoin acts as a store of value, similar to gold.
How to sell or buy using BitCoin
- Now let us take an example that you need to buy a Laptop and Shop owner accepts Bitcoin. Now to pay Shop owner you first need to know his public key (digital alphanumeric number).
- Then, using your private key, you initiate a transaction, which the shop owner receives using his own private key. Once the transaction completes, you get your laptop.
- Now let me explain this in a very easy way. You want to send some Coin to me. Then we both should have a public key or address and a very personal private key to authenticate transactions. Now to send using your private key you initiate a transaction to me by my public key. At the other end, I will use my private key to receive Coin.
- In the real world, people perform transactions using a Digital Wallet or Bitcoin-wallet, and the system automates and executes the above-shown transactions in a very user-friendly way. Moreover you will find an app for bitcoin in App store or Play store.
How to Buy or Sell Using Bitcoin
Buying or selling using Bitcoin is straightforward once you have a digital wallet. Here’s a simple step-by-step process:
- Get a Digital Wallet: Download a Bitcoin-wallet from the App Store or Play Store.
- Buy: Purchase Bit-coin from cryptocurrency exchanges using your local currency.
- Initiate Transactions: Use your private key to send Bitcoin to someone’s public key.
Examples of Usage:
- Buying goods and services online or in physical stores.
- Sending money across borders without hefty fees.
- Investing in it as a long-term asset.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bitcoin
This has revolutionized the financial landscape, but it comes with its own set of benefits and drawbacks.
Advantages:
- Decentralized: No government or bank interference.
- Transparency: Transactions are publicly recorded on the blockchain.
- Security: Cryptography ensures secure transactions.
- Lower Fees: No intermediaries mean minimal transaction costs.
Disadvantages:
- Volatility: Bitcoin’s value can fluctuate drastically.
- Regulatory Issues: Some governments have banned and some have heavily regulated it.
- Energy Consumption: Mining requires immense energy, raising environmental concerns.
- Complexity: Understanding Bitcoin and blockchain technology can be challenging for beginners.
Bitcoin Around the World: Who’s Using It?
It’s legal status varies across the globe.
- Countries That Accept Bitcoin:
- El Salvador (official currency)
- Japan
- Switzerland
- Germany
- Countries That Restrict Bitcoin:
- China
- Egypt
- Bangladesh
Why Some Countries Ban Bitcoin
Bitcoin’s anonymity can facilitate illicit activities such as money laundering and tax evasion. This has led some governments to impose restrictions or outright bans.
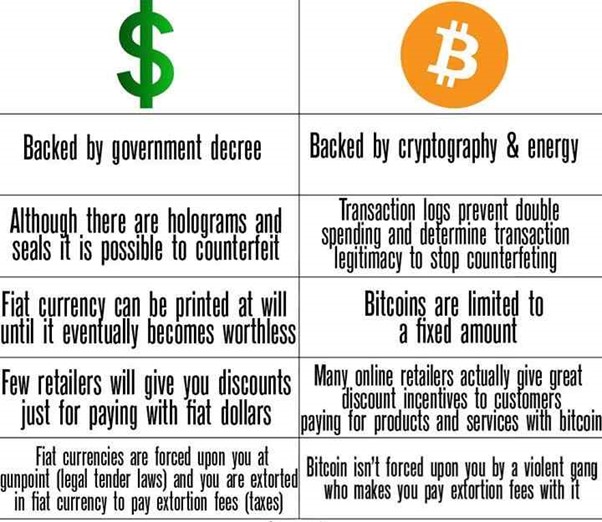
Why Choose, and Why Avoid It?
“Each and every transaction is secured and private. That means you don’t have to pay taxes or fees to the Government or Bank.”
- This is the prime reason some countries have not officially accepted Bit-coin and its transactions as a currency or money.
- While some countries have accepted it as currency and they do not prohibit transactions. They even allow buying or selling through.

Conclusion: Is Bitcoin the Future of Money?
Bitcoin has undeniably paved the way for a financial revolution. However, it’s important to approach it with caution, considering its risks, regulatory challenges, and market volatility.
If you’re interested, ensure you understand your country’s regulations and invest wisely.
While Bitcoin is not a physical currency, its impact on the financial world is tangible and profound.
As we move toward a more digital future, Bitcoin might just become the cornerstone of the global economy.
Till next time take care.
F.A.Q.
1. What happens when all 21 million Bitcoins are mined?
Once all 21 million Bitcoins are mined, no new Bitcoins will be created. Miners will rely on transaction fees for income instead of block rewards.
2. Can Bitcoin be hacked?
Bitcoin’s blockchain is virtually unhackable due to its decentralized nature and cryptographic security. However, individual wallets can be compromised if not secured properly.
3. Is Bitcoin legal in my country?
Bitcoin’s legal status varies by country. Check your local government’s regulations regarding cryptocurrencies before investing or transacting.
4. What is the difference between Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies?
Bitcoin is the first and most widely recognized cryptocurrency. Other cryptocurrencies, known as altcoins (e.g., Ethereum, Litecoin), have different use cases and features.
5. Can I lose my Bitcoin?
Yes. If you lose access to your private keys or digital wallet, you may permanently lose your Bit-coin. Always keep backups of your wallet information.

2u195o
ywfge8