Ever wonder why doctors, nutritionists, and even your mom always say, “Make sure you’re getting your vitamins!”? Well, there’s a reason for that!
Vitamins are like tiny superheroes small but mighty. They help keep your body running smoothly, from keeping your skin glowing to making sure your brain stays sharp.
Since your body can’t always make enough of them on its own, you need to get these essential nutrients from food (or sometimes supplements).
Now, let’s break it down:
The Two Main Types of Vitamins
There are 13 recognized vitamins, and they fall into two major categories:
- Fat-Soluble Vitamins (A, D, E, K) – These dissolve in fat and get stored in your body for later use.
- Water-Soluble Vitamins (C and the B vitamins) – These dissolve in water, meaning your body doesn’t store them, so you need to replenish them daily.
Let’s take a closer look at each group.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins: The Long-Term Players
These vitamins love fat literally.
Vitamins A, D, E, and K are absorbed along with fats in your diet and get stored in your liver and fatty tissues.
This means you don’t need to consume them daily, but too much of them can build up over time, which is why balance is key.
Quick Tip: Want to boost absorption? Eat fat-soluble vitamins with healthy fats like avocado, olive oil, or nuts!
- Vitamin A – Great for your eyes, skin, and immune system (found in carrots, sweet potatoes, and dairy).
- Vitamin D – The sunshine vitamin! Helps your body absorb calcium for strong bones.
- Vitamin E – A powerful antioxidant that protects your skin and cells.
- Vitamin K – Important for blood clotting and bone health.
Most people get enough of these through food, but if you rarely go outside (hello, office workers!), you might need a vitamin D supplement.
Water-Soluble Vitamins: The Daily Essentials
Unlike fat-soluble vitamins, water-soluble vitamins don’t get stored in your body. That means you need to replenish them every day through food or supplements.
The stars of this category? Vitamin C and the B-complex vitamins.
- Vitamin C – The ultimate immune booster! It also helps your body heal wounds and keeps your skin healthy. You’ll find it in citrus fruits, bell peppers, and strawberries.
- B Vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12) – These guys are the energy factories of your body, helping convert food into fuel. Each B vitamin has a special role:
- B12 & B9 (Folate) – Important for brain function and preventing anemia.
- B7 (Biotin) – Supports healthy hair, skin, and nails.
- B6 – Helps regulate mood and reduce PMS symptoms.
Did You Know?
Vegetarians and vegans often lack B12 since it’s mainly found in animal products. If that’s you, a supplement might be a good idea!
Should You Take a Vitamin Supplement?
Most people can get all the vitamins they need from a well-balanced diet. But there are some exceptions:
- If you have a restricted diet (vegan, vegetarian, or food allergies).
- If you spend very little time in the sun (hello, winter blues = low vitamin D).
- If you’re pregnant or trying to conceive (folate is crucial!).
- If you have digestive issues that make it harder to absorb nutrients.
If you’re unsure whether you need a supplement, it’s always best to talk to a doctor or a nutritionist.
Vitamins are the tiny but powerful nutrients that keep your body functioning at its best. Whether you get them from food or supplements, making sure you’re getting enough is key to feeling great, staying healthy, and having energy to power through your day.

Vitamin A: Your Vision’s Best Friend (But Don’t Overdo It!)
You know how your mom always told you to eat your carrots if you wanted good eyesight? Well, she wasn’t wrong! Carrots—and many other foods—are packed with Vitamin A, a nutrient that plays a crucial role in keeping your vision sharp and your skin glowing.
But Vitamin A isn’t just about your eyes. It’s a powerhouse nutrient that supports your immune system, promotes healthy skin, and even helps your body fight infections. Let’s break it down!
What Exactly Is Vitamin A?
Here’s where it gets interesting—Vitamin A isn’t just one thing. It’s actually a group of compounds called retinoids (from animal sources) and carotenoids (from plant-based foods).
Quick Breakdown:
- Retinoids (like retinol, tretinoin, and isotretinoin) – Found in animal products and easily used by the body.
- Carotenoids (like beta-carotene) – Found in fruits and vegetables, and the body converts them into Vitamin A when needed.
That’s why some food labels list Vitamin A as RAE (Retinol Activity Equivalents)—it’s a way to measure how much Vitamin A your body can actually use from different sources.
How Does Vitamin A Help Your Body?
- Protects Your Vision – Without enough Vitamin A, your night vision can get blurry, and in severe cases, it can lead to total blindness.
- Boosts Your Immune System – Helps your body fight infections and keeps your skin and gut lining strong.
- Supports Healthy Skin – Retinoids are famous in skincare for increasing cell turnover, fighting acne, and even reducing wrinkles.
- Promotes Growth & Reproduction – Essential for proper development in kids and plays a role in fertility.
Signs of Vitamin A Deficiency
If you’re not getting enough Vitamin A, your body will let you know! Some common deficiency symptoms include:
- Xerophthalmia – refers to a range of eye disorders caused by vitamin A deficiency. It can lead to night blindness, dryness of the conjunctiva and cornea, and in severe cases, corneal ulcers and blindness.
- Poor Night Vision – If you struggle to see in dim light, it could be a warning sign.
- Dry Eyes & Skin – Vitamin A helps your body produce moisture—without it, your skin and eyes can feel dry.
- Frequent Infections – Your immune system relies on Vitamin A to stay strong.
- Delayed Wound Healing – Since it helps with cell regeneration, a lack of Vitamin A can slow down healing.
Who’s most at risk?
Vegans, people with digestive disorders (like Crohn’s disease), and those with cystic fibrosis are more likely to develop a deficiency.
Can You Have TOO Much Vitamin A? – Overdose!
Vitamin A is fat-soluble, meaning your body stores the excess instead of flushing it out like water-soluble vitamins (such as Vitamin C).
Too much Vitamin A especially from supplements can cause toxicity. Symptoms include Headaches & Dizziness, Fatigue & Nausea, Liver Damage (in extreme cases), Birth Defects (if taken in high doses during pregnancy).
Best Dietary Sources of Vitamin A
Animal-Based (Preformed Vitamin A – Retinoids) includes Fish liver oil (one of the richest sources!), liver, Dairy products (milk, cheese, butter), Eggs.
Plant-Based (Provitamin A – Carotenoids) includes sweet potatoes (a single one gives you more than 100% of your daily Vitamin A!), Carrots, Kale, spinach, and other leafy greens, Cantaloupe and mangoes.
Good to know - A single sweet potato gives you more than 100% of your daily Vitamin A
How Much Vitamin A Do You Actually Need?
Recommended Daily Intake (According to ICMR India Guidelines):
| Age (years) | 1–3 | 4–8 | 9–13 | 14 and over |
| Male | 300 mcg RAE | 400 mcg RAE | 600 mcg RAE | 900 mcg RAE |
| Female | 300 mcg RAE | 400 mcg RAE | 600 mcg RAE | 700 mcg RAE |
Vitamin A is amazing for your vision, skin, and immune system, but too much can be harmful. The best way to get enough? Eat a balanced diet full of colourful veggies, dairy, and healthy fats.
What Is Vitamin B-Complex?
Ever wonder why B vitamins seem to be in almost every energy drink and supplement out there?
That’s because this group of nutrients is like your body’s natural fuel system helping convert food into energy, keeping your brain sharp, and even promoting healthy skin and hair.
But here’s the catch: Your body doesn’t store most B vitamins, so you need to get them from food or supplements every day.
Let’s dive into what makes the Vitamin B-complex so important, who might need a supplement, and how to get the right balance.
Vitamin B isn’t just one vitamin, it’s actually a group of eight essential vitamins that each play a unique role in your health.
Together, they form what’s called the B-complex, which supports everything from metabolism to mental health.
The 8 Types of B Vitamins and What They Do:
- Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) – The Brain Booster
Keeps your brain and heart functioning properly. Without enough B1, you might feel weak, have trouble focusing, or experience nerve damage.
- Vitamin B2 Riboflavin (Yellow vitamin) – The Migraine Fighter
Breaks down fats and may help prevent migraines by improving cellular function. Found in dairy, eggs, and leafy greens.
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin) – The Skin & Cholesterol Helper
Doctors sometimes prescribe high doses of niacin to lower cholesterol.
It also improves skin texture and reduces signs of aging. FYI, Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a vital coenzyme found in all living cells that plays a key role in energy production, DNA repair, and cellular aging.
As we age, NAD levels decline, which has been linked to aging and metabolic disorders, which can be compensated by NAD supplements.
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) – The Stress Buster
Essential for brain function and stress management. Helps reduce acne and hyperpigmentation.
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) – The Mood Regulator
Supports red blood cell production and plays a role in reducing PMS symptoms and depression.
- Vitamin B7 (Biotin or Vitamin H) – The Hair & Nail Strengthener
Commonly found in beauty supplements—great for hair growth, strong nails, and healthy skin.
- Vitamin B9 (Folate/Folic Acid) – The Pregnancy Protector
Crucial for DNA production and prevents birth defects in pregnancy. Found in spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals.
- Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) – The Energy & Nerve Supporter
Keeps nerve cells and red blood cells healthy. Deficiency is common in vegans and older adults and can lead to fatigue, memory loss, and anemia.
Who Needs a B-Complex Supplement?
Most people get enough B vitamins from a balanced diet, but certain groups are more at risk for deficiency.
Since B12 is mainly found in animal products, plant-based eaters (Vegans & Vegetarians) should take a supplement.
The ability to absorb B12 declines with age, increasing the risk of memory issues in Older Adults, senior citizens.
Pregnant Women need extra folic acid (B9) to prevent birth defects.
Conditions like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease can reduce vitamin absorption in People with Digestive Disorders.
Consumption of Alcohol interferes with B-vitamin absorption, which leads to vitamin B deficiencies.
A lack of B vitamins can show up in surprising ways. Common symptom related to Vitamin B deficiency are Fatigue & Weakness (low B12), Tingling or Numbness in Hands & Feet (low B12), Irritability or Depression (low B6 & B12), Dry Skin or Cracked Lips (low B2), Mouth Ulcers & Burning Sensation in the Tongue (low B12), Headaches & Dizziness (low B2).
If you experience any of these, a simple blood test can check your B-vitamin levels.
Best Dietary Sources of B Vitamins
- Animal Sources: Beef, pork, eggs, fish, dairy products
- Plant-Based Sources: Leafy greens, avocados, nuts, whole grains, beans, mushrooms
- Fortified Foods: Cereals, soy milk, nutritional yeast
Pro Tip: Since B12 is only found in animal products, vegans should eat fortified foods or take a supplement such as vitamin B12 tablets.
Overdose on Vitamin B?
Too much of anything is bad including B vitamins.
Since Vitamin B is water-soluble, your body flushes out the excess, but extreme doses (especially from supplements) can cause side effects like Flushing & Skin Rash (excess B3), Liver Damage (high-dose B3 from supplements), Nerve Problems & Tingling (excess B6), Diarrhoea & Stomach Issues (too much B5).
Vitamin B complex helps in maintaining Glowing Skin & Anti-Aging. B3 (Niacinamide) and B5 help reduce wrinkles, dark spots, and acne.
Many skincare products contain B vitamins for this reason! Biotin (B7) is famous for promoting thicker hair and preventing brittle nails.
Low B6 and B12 levels have been linked to depression and anxiety. Some studies suggest that B vitamins can help lower the risk of depression relapse.
If you’re getting enough B vitamins from food, you probably don’t need a supplement. But if you’re vegan, pregnant, an older adult, or have absorption issues, a B-complex might boost your energy, brain function, and overall health.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in the body’s overall health. From boosting the immune system to promoting collagen production, this essential nutrient is key to maintaining optimal health and wellness.
Unlike fat-soluble vitamins, which are stored in the body’s fat tissues, vitamin C must be consumed daily because it is not stored in the body.
One of the most significant benefits of vitamin C is its role as an antioxidant.
Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals, which are unstable molecules that cause oxidative stress and damage to cells. This process is linked to aging, inflammation, and various chronic diseases.
By consuming vitamin C rich foods or supplements, individuals can help protect their cells from oxidative damage and promote better overall health.
Vitamin C is well-known for its ability to enhance immune function. It helps stimulate the production of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections and diseases. Studies have shown that regular vitamin C intake may help:
- Reduce the severity and duration of colds and flu
- Enhance the body’s ability to fight infections
- Strengthen the body’s natural defence mechanisms against harmful pathogens
While vitamin C alone may not prevent colds, it can help reduce symptoms and recovery time, making it an essential nutrient for immune system support.
Vitamin C is a key player in tissue repair and wound healing. It is required for collagen production; a protein that helps wounds heal faster by forming new connective tissues.
People recovering from surgery, burns, or injuries often need higher vitamin C intake to speed up the healing process and reduce the risk of infections.
Vitamin C and Cardiovascular Health
Heart disease is a leading cause of death worldwide, and vitamin C plays an essential role in maintaining cardiovascular health. Some of its benefits include:
- Lowering blood pressure: Vitamin C helps relax blood vessels, improving circulation and reducing hypertension.
- Reducing inflammation: Chronic inflammation contributes to heart disease, and vitamin C helps combat it by reducing oxidative stress.
- Lowering cholesterol levels: Vitamin C may help decrease bad cholesterol (LDL) and increase good cholesterol (HDL), improving overall heart health.
Vitamin C’s Role in Iron Absorption
Iron is an essential mineral that helps transport oxygen in the blood, but many people, especially vegetarians and vegans, struggle with iron absorption from plant-based sources.
Vitamin C significantly enhances the body’s ability to absorb iron, preventing deficiencies and reducing the risk of iron-deficiency anaemia.
Consuming vitamin C-rich foods alongside iron-rich foods, such as spinach or lentils, can maximize absorption and prevent fatigue caused by low iron levels.
How Vitamin C Supports Brain Health
Studies suggest that vitamin C plays a role in cognitive function and may help prevent neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. This essential vitamin supports brain health by:
- Reducing oxidative stress in the brain
- Enhancing neurotransmitter function
- Protecting against age-related cognitive decline
Getting enough vitamin C in the diet may contribute to better memory, focus, and overall mental sharpness as we age.
Vitamin C for Healthy and Youthful Skin
One of the most well-known benefits of vitamin C is its anti-aging effects on the skin.
This vitamin is essential for collagen production, which keeps the skin firm, smooth, and youthful.
Benefits of Vitamin C for Skin
Vitamin C Reduces wrinkles and fine lines by increasing collagen production. It Protects against sun damage by neutralizing free radicals caused by UV rays.
This vitamin Brightens skin tone and reduces hyperpigmentation. While vitamin C serum can help to reduce the appearance of a tan and even out skin tone, it won’t completely remove a tan on its own. Overall, it Improves skin hydration and elasticity.
Many vitamin C serums and skincare products are popular because they help restore skin’s natural glow while protecting against environmental damage.
Vitamin C promotes collagen production, reduces wrinkles, and brightens skin tone.
While it doesn’t completely prevent colds, vitamin C can reduce symptoms and shorten the duration of illness.
Vitamin C Deficiency: What You Need to Know
A lack of vitamin C can lead to scurvy, a condition with symptoms such as Fatigue and weakness, Bleeding gums and tooth loss, Slow wound healing, Skin problems and easy bruising.
Since the body does not store vitamin C, it’s essential to consume enough through food or supplements to prevent deficiency and maintain good health.
Best Food Sources of Vitamin C
Vitamin C is found naturally in many fruits and vegetables. Here are some of the best dietary sources:
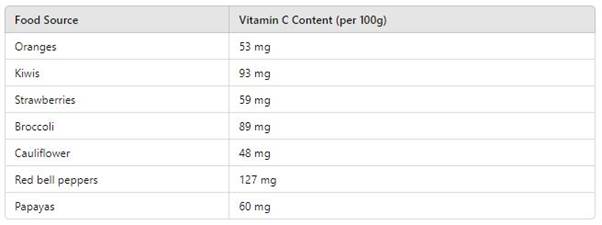
Including a variety of these foods in your diet can help ensure adequate vitamin C intake and support overall health.
Should You Take a Vitamin C Supplement?
While it’s best to get nutrients from whole foods, some people may benefit from vitamin C supplements, especially those with Poor dietary intake, High stress levels, Frequent colds or infections, Skin concerns or aging signs
Most multivitamins contain vitamin C, but standalone vitamin C supplements are available in tablet, vitamin C capsule, and powder forms.
How Much Vitamin C Do You Need Daily?
The recommended daily intake of vitamin C varies by age and gender:
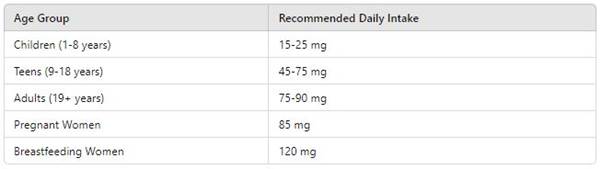
Whole foods are always the best source, but supplements can help fill dietary gaps if needed.
Sometimes heat and light can degrade vitamin C, so it’s best to eat some raw fruits and vegetables daily.
Smokers require an additional 35 mg per day due to increased oxidative stress from cigarette smoke. It can be taken any time of the day, but it’s best with meals to enhance absorption.
Excess vitamin C is usually excreted in urine, but very high doses may cause stomach upset, diarrhoea, and kidney stones.
Vitamin C is a powerful nutrient with countless health benefits. From boosting immunity and supporting heart health to improving skin and brain function, this essential vitamin plays a vital role in overall well-being.
Make sure to include enough vitamin C in your diet daily to stay healthy, vibrant, and energized!
Vitamin D: The Sunshine Vitamin for Strong Bones and a Healthy Immune System
When we think about staying healthy, we often focus on eating right, exercising, and getting enough sleep. But there’s one crucial nutrient that sometimes flies under the radar Vitamin D.
This powerhouse vitamin is essential for bone health, immune function, and even skin repair.
But did you know that Vitamin D isn’t just one single substance? It’s actually a group of compounds known as calciferol, which our bodies absorb and convert into an active form called calcitriol.
Types of Vitamin D: Where Do We Get It?
There are two main types of naturally occurring Vitamin D:
- Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) – Found in animal-based foods like fatty fish and egg yolks.
- Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) – Found in plant sources, such as mushrooms.
Unlike most vitamins that we get mainly from food, Vitamin D is unique because our bodies can produce it when exposed to sunlight. That’s why it’s often called the “sunshine vitamin.”
But even though sunlight is the best natural source, modern lifestyles spending most of our time indoors, wearing sunscreen, and living in places with long winters often lead to deficiencies.
Why Does Your Body Need Vitamin D?
- Vitamin D plays a crucial role in many body functions, including:
Bone Health – Helps the body absorb calcium and phosphorus, which are vital for strong bones and teeth. - Immune Support – Strengthens the immune system, reducing the risk of infections.
- Skin Repair – Aids in skin cell metabolism, growth, and repair.
- Inflammation Control – May help reduce chronic inflammation, which can lead to conditions like acne and eczema.
Vitamin D deficiency can affect anyone, but it’s more common in Older adults, People who stay indoors most of the time, Those with darker skin (as melanin reduces Vitamin D production from sunlight), Individuals with medical conditions that affect nutrient absorption.
What Happens When You Don’t Get Enough?
The most serious effects of Vitamin D deficiency include:
- Osteoporosis – A condition where bone density decreases, making bones weak and brittle. This is more common in older adults, especially postmenopausal women.
- Osteomalacia (in adults) & Rickets (in children) – A condition where bones become soft and weak, leading to pain and an increased risk of fractures. In children, rickets can cause bone deformities and growth problems.
- Increased Risk of Infections – Since Vitamin D plays a role in immune function, low levels may make you more prone to getting sick.
How Much Vitamin D Do You Need?
The recommended daily intake for Vitamin D is 600 IU (International Units) for most people. However, some experts suggest that individuals with limited sun exposure may need more.
Best Sources of Vitamin D
Since Vitamin D isn’t naturally present in most foods, you’ll need to get it from a mix of sources:
While most vitamins are sourced from food, sunlight plays a vital role in the production of vitamin D. The human body synthesizes the vitamin when exposed to sunlight, and this is the best source of vitamin D.
Dietary sources include oily fish and fish oils, fortified dairy products, plant-based milks, and cereals, beef liver, eggs. Beneficial sources of vitamin D include fortified products such as milk and cereal, as well as salmon, swordfish, and tuna.
If you live in a place with limited sunlight, have a darker skin tone, or follow a strict plant-based diet, you may not be getting enough Vitamin D.
Adding fortified foods to your diet and spending a little time outdoors can make a huge difference in your overall health.
Can You Take Too Much Vitamin D?
Yes! While Vitamin D is essential, too much of it can be harmful—especially if taken in high doses through supplements.
Vitamin D toxicity can lead to high calcium levels in the blood (hypercalcemia), causing nausea and vomiting, Loss of appetite and weight loss, Headaches and fatigue, Kidney and heart problems.
Vitamin E: The Antioxidant Powerhouse for Healthy Skin, Immunity
When it comes to essential nutrients, Vitamin E is a bit of an unsung hero.
While it doesn’t always get as much attention as Vitamin C or D, this powerful antioxidant plays a huge role in keeping your body healthy.
From supporting your immune system to keeping your skin glowing, Vitamin E is a must-have in your diet.
What Exactly Is Vitamin E?
Vitamin E isn’t just one thing, it’s actually a group of eight different compounds.
However, for humans, only alpha-tocopherol is important.
This is the form of Vitamin E that our bodies recognize and use to perform vital functions.
Why Does Your Body Need Vitamin E?
Vitamin E is a powerhouse nutrient with many health benefits, including:
- Boosting the Immune System – Helps your body fight off infections and illnesses.
- Keeping Blood Flow Healthy – Dilates blood vessels and helps prevent clotting.
- Protecting Cells from Damage – Acts as a strong antioxidant, reducing damage caused by free radicals (unstable molecules that can harm cells).
- Slowing Signs of Aging – May help reduce wrinkles and improve skin texture by fighting oxidative stress.
- Healing Wounds & Scars – Used in skincare for its potential role in wound healing, especially when combined with Vitamin C and zinc.
- Supporting Nerve & Muscle Function – Helps maintain coordination, vision, and muscle strength.
Vitamin E & Skin Health: A Natural Glow Booster
You’ve probably seen Vitamin E listed in skincare products—and for good reason!
Preliminary research suggests that it may Slow skin aging by reducing damage from UV rays and pollution.
It Help fade scars and moisturize dry skin. Improve wound healing, especially when combined with Vitamin C and zinc.
Soothe acne and pressure sores, though more research is needed.
What Happens If You Don’t Get Enough Vitamin E?
Vitamin E deficiency is rare, but it can affect people with Crohn’s disease, cystic fibrosis, or any condition that affects fat absorption. A long-term deficiency can lead to:
- Nerve and muscle damage – Can affect movement and coordination.
- Vision problems – Weakens the ability to see clearly.
- Weakened immune system – Increases the risk of infections.
- Higher risk of chronic diseases – Since Vitamin E is an antioxidant, a deficiency may contribute to conditions linked to oxidative stress, like heart disease.
Best Sources of Vitamin E
Luckily, Vitamin E is easy to get from a healthy diet. Some of the best natural sources include Nuts & Seeds i.e. Almonds, hazelnuts, sunflower seeds, peanuts; Vegetables like Spinach, broccoli, corn; Fruits like Mangoes, kiwis; Oils & Grains like Wheat germ oil, sunflower oil.
For most people, a balanced diet provides enough Vitamin E, it is also available as a vitamin e capsule.
How Much Vitamin E Do You Need?
The recommended daily intake (measured in milligrams (mg) alpha-tocopherol (AT)) is as under.
| Age (Years) | Daily Vitamin E Intake |
| 1–3 years | 6 mg (9 IU) |
| 4–8 years | 7 mg (10.4 IU) |
| 9–13 years | 11 mg (16.4 IU) |
| 14 and older | 15 mg (22.4 IU) |
Can You Get Too Much Vitamin E?
Getting Vitamin E from food alone is unlikely to cause an overdose.
However, taking high-dose supplements can be risky. Excess Vitamin E can lead to Increased bleeding risk (because it can thin the blood), Potential interference with blood-thinning medications.
If you take blood thinners or other medications, talk to your doctor before using Vitamin E supplements.
Vitamin K: The Essential Nutrient for Blood Clotting and Bone Health
When we talk about essential vitamins, Vitamin K often takes a backseat to its more famous counterparts like Vitamin C or D. But don’t underestimate its importance!
This fat-soluble vitamin plays a vital role in blood clotting, bone strength, and heart health.
Unlike some other vitamins, your body doesn’t store large amounts of Vitamin K, which means you need a steady intake from your diet to stay healthy.
Types of Vitamin K: What’s the Difference?
There are several forms of Vitamin K, but the two most common are:
- Vitamin K-1 (Phylloquinone) – Found in green leafy vegetables like spinach, kale, and parsley.
- Vitamin K-2 (Menaquinones) – Found in animal products and fermented foods like liver, butter, egg yolks, and natto (fermented soybeans).
Your gut bacteria can also produce small amounts of Vitamin K-2, but not enough to meet your daily needs. There are also synthetic forms of Vitamin K, used in supplements and medical treatments.
Why Do You Need Vitamin K?
Vitamin K is best known for its role in blood clotting, but its benefits go beyond just stopping excessive bleeding. It also:
- Supports Blood Clotting – Helps wounds heal by ensuring your blood clots properly.
- Strengthens Bones – Works with calcium and Vitamin D to improve bone density and reduce the risk of fractures.
- Boosts Heart Health – May help prevent calcium buildup in arteries, reducing the risk of heart disease.
What Happens If You Don’t Get Enough?
Since Vitamin K isn’t stored in large amounts, a deficiency can develop quickly if you don’t get enough from food.
- Excessive Bleeding – Because Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting, a deficiency can led to easy bruising, nosebleeds, or prolonged bleeding from cuts or injuries.
- Lower Bone Density – Not enough Vitamin K can increase the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
- Potential Heart Issues – Some studies suggest that low Vitamin K levels may lead to a higher risk of arterial calcification, which could contribute to heart disease.
People at a higher risk of Vitamin K deficiency include:
- Newborns (who are often given a Vitamin K shot at birth)
- People with digestive disorders like Crohn’s disease or celiac disease (which can affect nutrient absorption)
- Those taking long-term antibiotics (which can kill the gut bacteria that help produce Vitamin K)
Best Food Sources of Vitamin K
The best way to get Vitamin K is through a well-balanced diet.
Vitamin K-1 is found in Plant Based Sources such as Kale, Spinach, Parsley, Broccoli and Brussels sprouts.
Vitamin K-2 is found in Animal & Fermented Foods such as Liver, Butter, Egg yolks, fermented soybeans, and Cheese.
The best way to get enough Vitamin K is through a healthy, balanced diet rich in leafy greens, vegetables, and fermented foods.
While supplements can help in certain situations, they shouldn’t replace natural food sources unless recommended by a doctor.
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin K varies based on age and gender.
| Age (years) | 1–3 | 4–8 | 9–13 | 14–18 | 19 and over |
| Male | 30 IU | 55 IU | 60 IU | 75 IU | 120 IU |
| Female | 30 IU | 55 IU | 60 IU | 75 IU | 90 IU |
Can You Take Too Much Vitamin K?
Unlike some vitamins (like A or D), Vitamin K toxicity is rare because excess amounts are usually excreted. However, taking high doses through supplements can be a problem, especially for people on blood-thinning medications.
Too much Vitamin K can Interfere with blood thinners, making them less effective. Moreover, it increases the risk of excessive clotting, which can be dangerous for people at risk of stroke or heart disease.
The best way to get enough Vitamin K is through a healthy, balanced diet rich in leafy greens, vegetables, and fermented foods.

Conclusion
Vitamins play a huge role in keeping us healthy they boost our immune system, keep our energy levels up, and help prevent a bunch of health issues.
The best way to get all the vitamins your body needs?
A balanced diet packed with colourful fruits, fresh veggies, whole grains, and good sources of protein.
But if your body isn’t getting enough of certain vitamins, it can lead to some pretty serious health problems. That’s why it’s important to pay attention to any warning signs and tweak your diet when needed.
Nowadays vitamin supplements are available in the form of vitamin patches which offers a convenient, needle-free way to absorb nutrients directly through the skin, potentially improving absorption for those with digestive issues.
However, their effectiveness varies, as research on transdermal vitamin delivery is still limited, and some nutrients may not absorb well through the skin.
Want to stay on top of your health? Stick to real, nutrient-rich foods, and if you’re ever unsure about a deficiency, checking in with a healthcare professional is always a good idea.
Take care.
How to Get Fit & Fabulous

Si eres fanatico de los sitios de apuestas en linea en Espana, has llegado al portal correcto.
En este sitio encontraras analisis completos sobre los plataformas mas seguras disponibles en Espana.
### ?Por que elegir un casino espanol?
– **Casinos regulados** para jugar con seguridad garantizada.
– **Bonos de bienvenida exclusivos** que aumentan tus posibilidades de ganar.
– **Amplia variedad de juegos** con premios atractivos.
– **Pagos rapidos y seguros** con multiples metodos de pago, incluyendo tarjetas, PayPal y criptomonedas.
?Donde encontrar los mejores casinos?
En nuestro blog hemos recopilado las **resenas mas completas** sobre los mejores casinos en linea de Espana. Consulta la informacion aqui: .
**Registrate hoy en un casino de prestigio y descubre una experiencia de juego unica.**
Ready to transform your style with genuine dreadlocks? Explore this range of dread natural at this link – handmade dreadlocks, offering the highest quality options for achieving a flawless, natural look.
Made with 100% human hair, these dreadlocks are ideal for natural styling. Whether you’re into full-head transformations, we have options that fit curly, coily, or straight textures.
Choose your vibe with:
– dread natural
– dreads real hair
Stand out confidently with premium-quality extensions that look and feel real. Smooth checkout available across the USA and beyond!
Claim yours today – your dream style awaits.
Your blog is a testament to your dedication to your craft. Your commitment to excellence is evident in every aspect of your writing. Thank you for being such a positive influence in the online community.
I am really inspired with your writing skills as well as with the structure on your weblog.
Is that this a paid subject or did you modify it yourself?
Anyway stay up the nice high quality writing, it is rare to look a nice weblog like this one
today. HeyGen!
Looking to refresh your hairstyle with genuine dreadlocks? Check out a stunning range of dreads real hair at this link – https://williambedrosartisan.site/real-dreadlocks-for-sale-authentic-high-quality-dreads-at-daddy-dreads/, offering the highest quality options for achieving a flawless, natural look.
Expertly hand-crafted with 100% human hair, these dreadlocks are ideal for self-expression through hair. Whether you’re into full-head transformations, we have options that suit your exact texture.
Choose your vibe with:
– real dreadlock extensions
– dreadlock extensions
Stand out confidently with premium-quality extensions that look and feel real. Smooth checkout available across the USA and beyond!
Start your journey – your dream style awaits.
Looking to upgrade your vibe with authentic dreadlocks? Browse the best range of handmade dreadlocks at this page – human hair dreadlock extensions, offering the highest quality options for achieving a flawless, natural look.
Expertly hand-crafted with ethically sourced hair, these dreadlocks are a great match for natural styling. Whether you’re into temporary installs, we have options that suit your exact texture.
Choose your vibe with:
– real dreadlock extensions
– dreads real hair
Achieve that natural dreadlock vibe with premium-quality extensions that look and feel real. Discreet packaging available across the USA and beyond!
Start your journey – your new hair era starts here.
awesome
Do you mind if I quote a few of your articles as long
as I provide credit and sources back to your webpage?
My blog iis in the exact same area off interest as yours and my visitors would certainly benefit from a lot of the information you present here.
Pleaee let me know if this okay with you. Thank you! http://Boyarka-Inform.com/
a86kf5
uhi67d